AI Seat Analytics & Horse Rider Biomechanics
Horse rider biomechanics is the study of how the rider’s body moves and interacts with the horse while riding. It involves the analysis of the posture, balance, and movement patterns of both the horse and rider, as well as the impact of the rider’s weight, position, and actions on the horse’s movement and well-being. Good biomechanics is important for improving performance, reducing the risk of injury, and enhancing the horse’s comfort and welfare.
Establishing a ‘correct’ riding position is incredibly important, from the moment we mount our horses.
For dressage riders, the perfect dressage position is a balanced, elegant posture, quiet hands, with the legs close to the horse’s sides. The rider’s seat should be deep and still, the weight distributed evenly over both seat bones, with a slight flexion at the hip, knee, and ankle joints. The arms are relaxed and extended forward, with the reins held lightly. This position allows the rider to maintain control and communicate effectively with the horse while promoting the horse’s comfort, flexibility, and self-carriage.

How does this relate to the feedback given by the AI Seat Analytics tool?
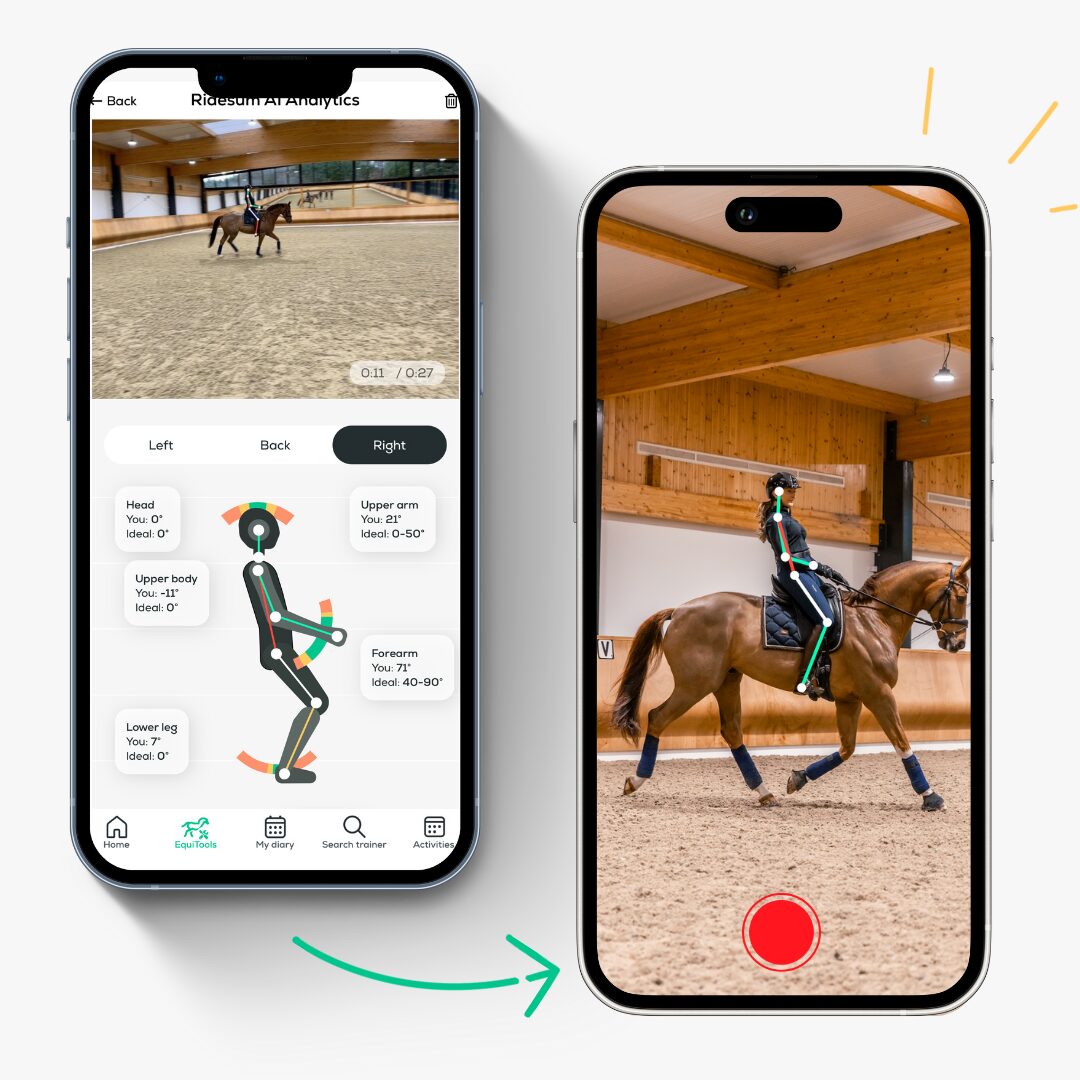
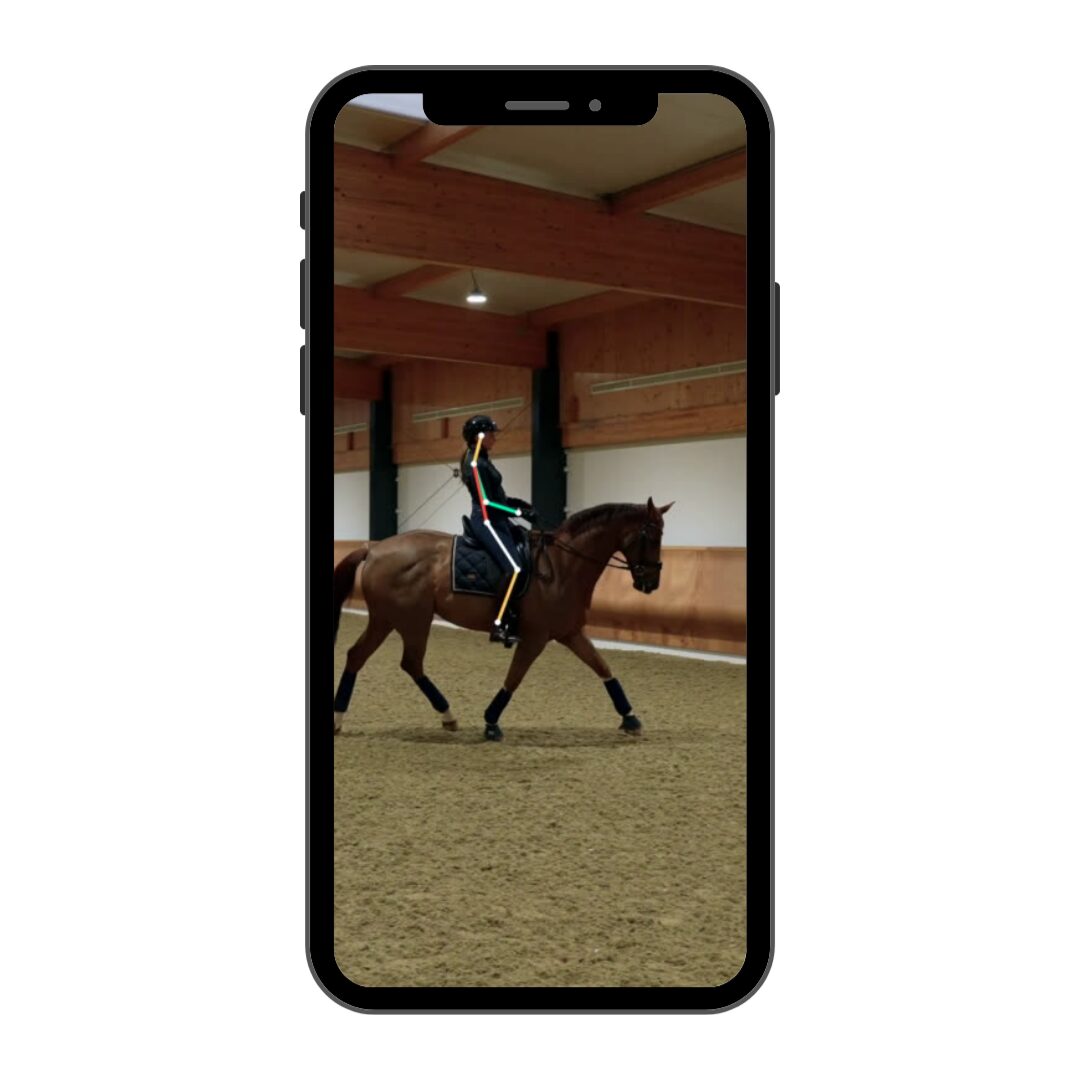
The Ridesum equestrian app analyses the rider’s position from the side and from the front/back.
Side-View
The app automatically detects the key joints on a horse rider’s body when filmed from the side. It collects data from every frame of a video (or recording period for the live capture) and then takes an average. This lets the app measure key metrics, analysing rider posture along the following classical Dressage guidelines:
- Head position: is there a straight vertical line from the ears to the shoulders?
- Upper arm position: are the elbows slightly in front of the body?
- Forearm: is there enough bend in the elbows?
- Upper body position: is there a straight vertical line from shoulder to hip?
- Lower leg position: is there a straight vertical line from hip to heel?
- Foot position: is the heel slightly down?
The app automatically generates a diagram that represents the rider’s average position/ angles throughout the video. This diagram and the results table are both colour coded:
- Green indicates a good dressage position.
- Yellow indicates an acceptable dressage position.
- Red indicates a position that needs improvement.
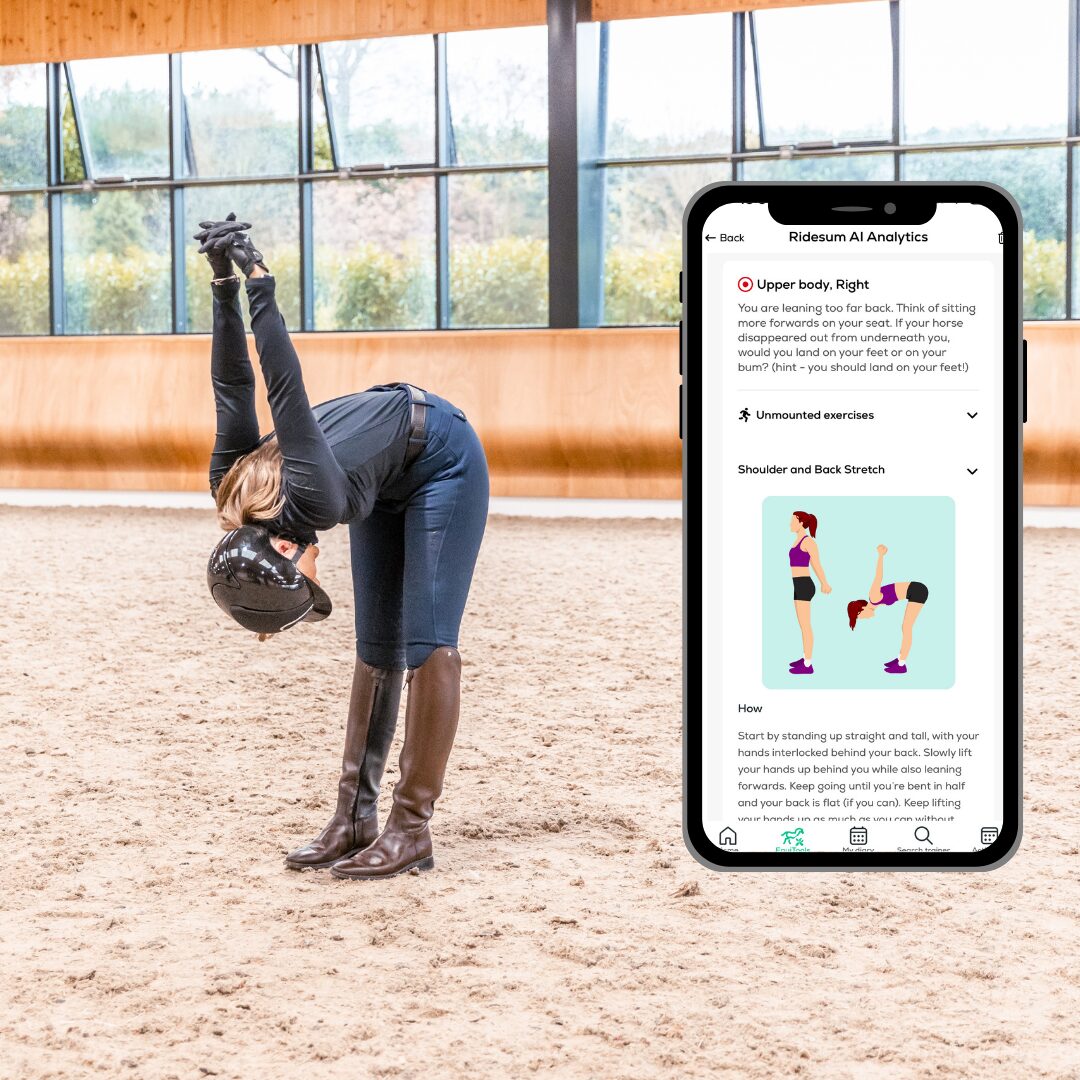
Based on your analysis results, the app will give you suggestions for exercises or stretches that may help you to improve your position.

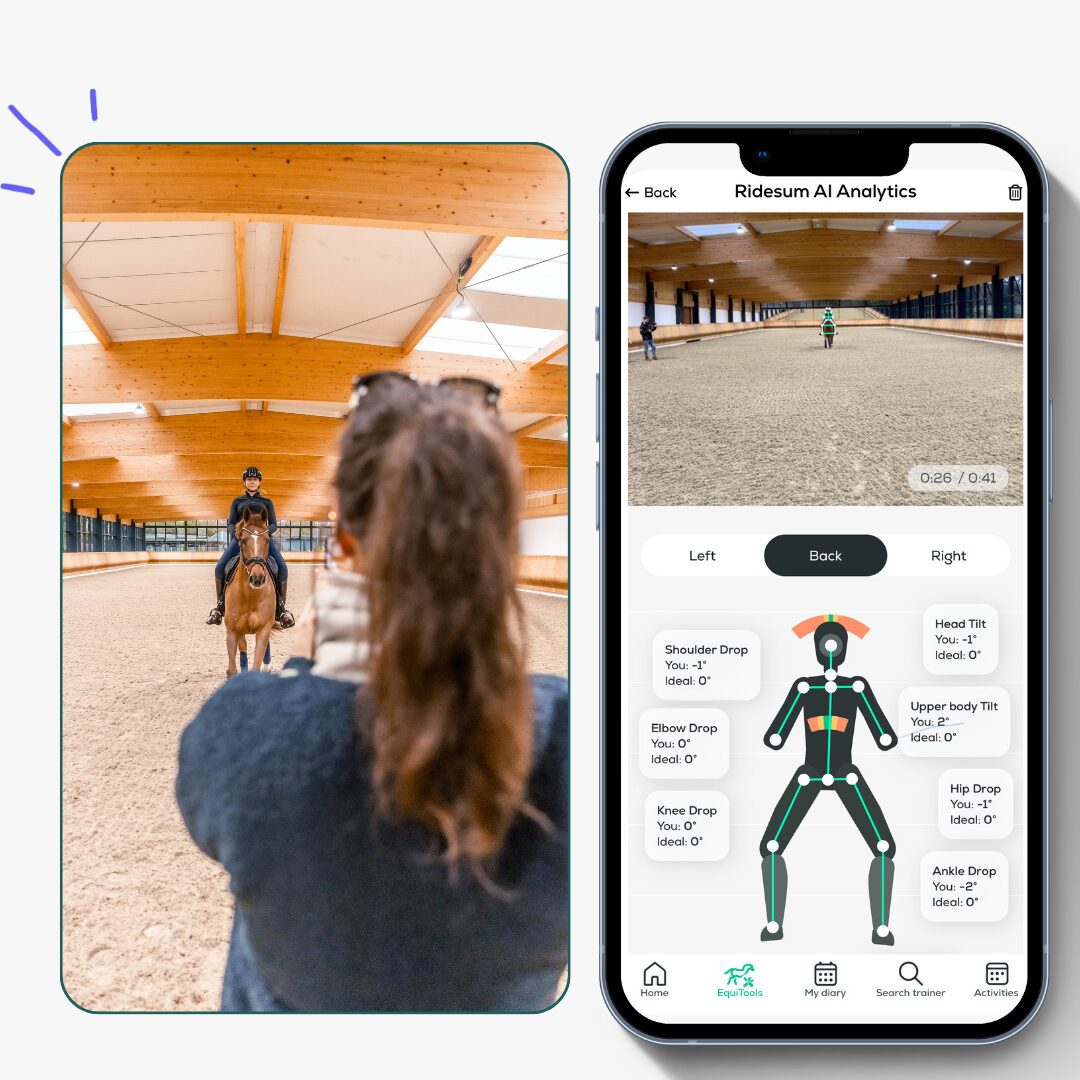
Front or Back View
As for the view from the side, the app automatically detects the key joints on a rider’s body when filmed directly from the back or front. This lets the app measure key metrics, analysing rider position and determine the following:
- Head is level or if it is tilted
- Shoulders are level
- Elbows and hands are held at the same level
- Hips are level and even
- Knees and ankles are at the same level
- Upper body straight or do they lean to one side?
Similarly to the side view, the app generates a colour coded diagram that represents the rider position on average throughout the video along with a table of the actual average angles.
Note that the app cannot always accurately see the rider’s knees and ankles if filming from the back or the front. In these situations, the app will report these values as N/A.
The ‘perfect’ dressage position should entail the following:
- The head is directly above the shoulders (target angle is 0°).
- The upper arm should be just in front of the body, but not too straight (target angle between 0 and 50.
- The forearm should be just lower than the elbow (target angle between 40 and 90°)
- The upper body should be straight, shoulders above hips (target angle 0°)
- The lower leg should be directly below the hip (target angle 0°)
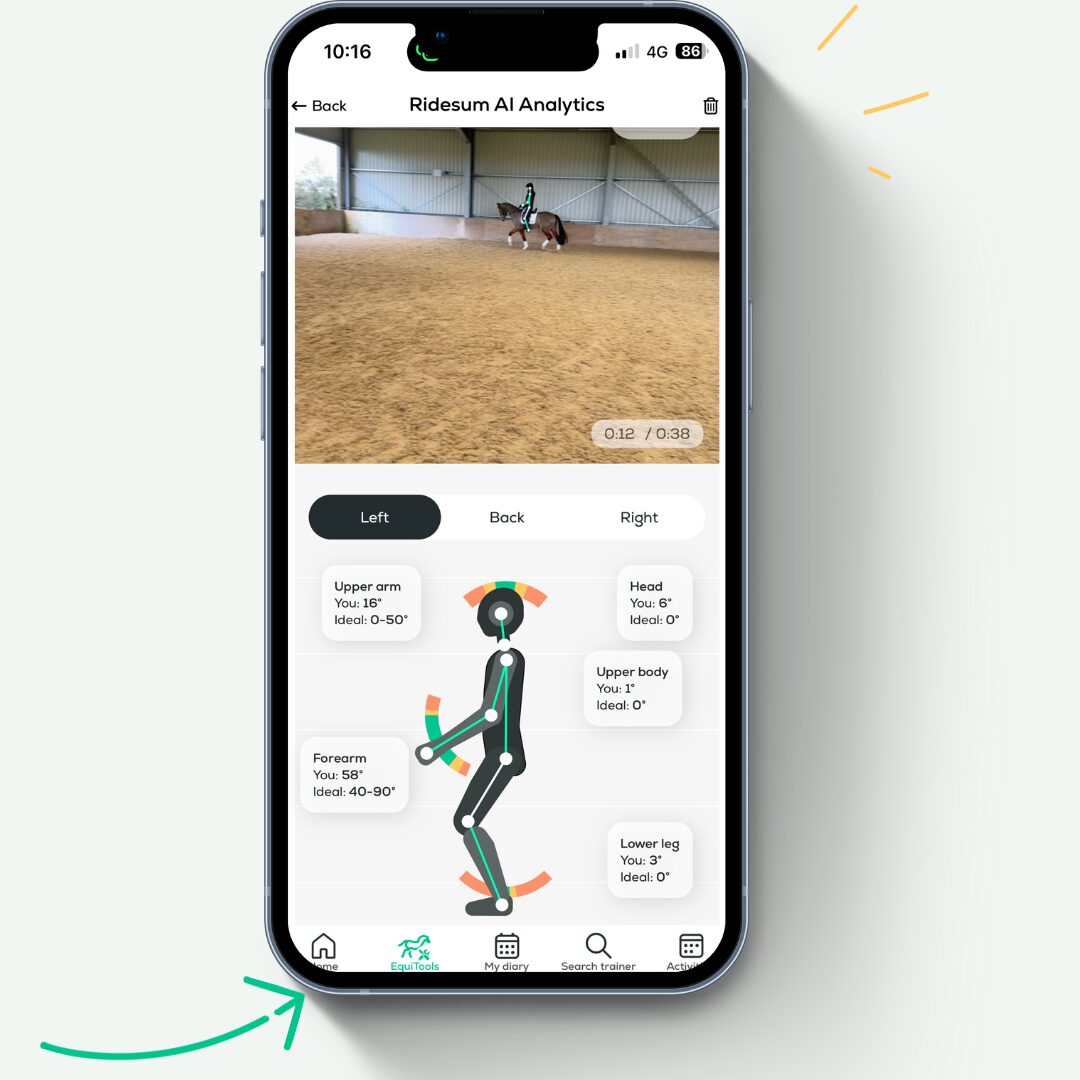
Here is an example of the post-analysis results, demonstrating a ‘good’ dressage position with no deviations, as viewed from the side:
- Head: 6°
- Forearm: 58°
- Upper arm: 16°
- Upper body: 1°
- Lower leg: 3°
Here is another example of a riding position which can be improved upon, here the rider is tipping a little too far backwards, highlighted red, negative angle of -11°.